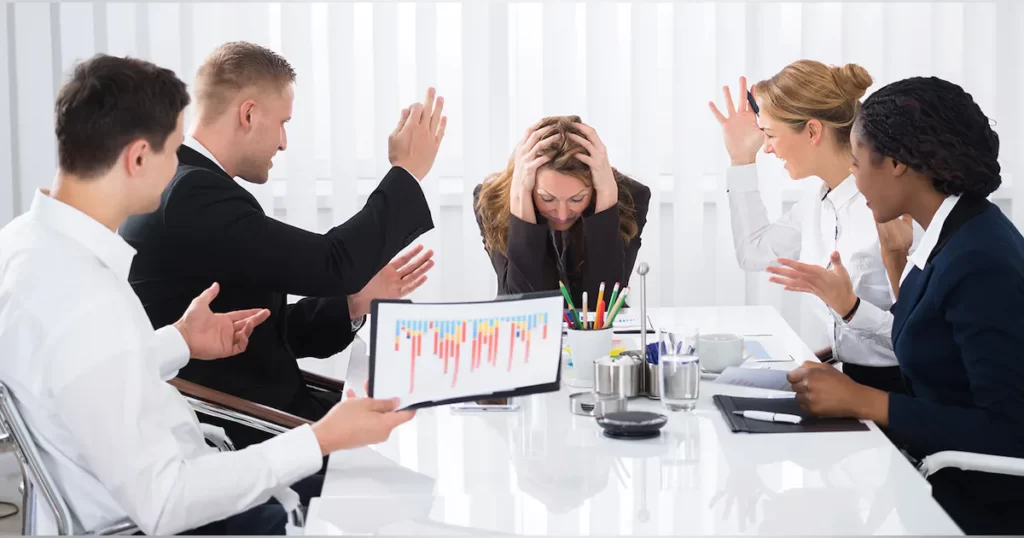
Workplace bullying: A silent epidemic lurking in the shadows of our professional lives. This subtle yet destructive force has far-reaching consequences, often leaving deep psychological scars. According to a 2020 survey by the Workplace Bullying Institute, 19% of U.S. workers reported experiencing bullying directly, making it a pressing issue that needs immediate attention.
Defining Workplace Bullying
In essence, workplace bullying is a pattern of persistent and harmful behavior directed at an individual in a professional environment. It can take on various forms – overt or covert, verbal or non-verbal, online or offline. This includes overtly aggressive acts like public humiliation, offensive remarks, or personal attacks, as well as more subtle forms of bullying like spreading rumors, isolating an individual, or setting unrealistic work demands.
The Impact on the Individual
The repercussions of workplace bullying on the targeted individual are profound and multidimensional. Victims often suffer from a range of psychological issues, including anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder. A study published in the Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine even found that bullied employees were twice as likely to harbor suicidal thoughts compared to their non-bullied counterparts.
Physically, the stress and anxiety from being bullied can lead to insomnia, high blood pressure, and other stress-related illnesses. It can also negatively affect the victim’s personal relationships and overall quality of life.
The Impact on the Organization
Workplace bullying doesn’t just harm the individual – it corrodes the very fabric of the organization. A toxic work environment can lead to decreased productivity, increased absenteeism, and high staff turnover, all of which cost businesses significantly. According to a SHRM report, workplace bullying costs U.S. businesses close to $250 million annually in lost time and productivity.
Legal Implications of Workplace Bullying
While there’s no federal law specifically against workplace bullying in the United States, victims may seek legal redress under laws prohibiting discrimination and harassment. In some states, there are efforts to enact the “Healthy Workplace Bill,” which would make severe workplace bullying illegal. Understanding the legal landscape related to workplace bullying is crucial for both employees and employers to protect their rights and interests.
Strategies to Address Workplace Bullying
Addressing workplace bullying requires a comprehensive, organization-wide approach. Here are some strategies:
- Developing a Robust Anti-Bullying Policy: This policy should explicitly define bullying behaviors, establish procedures for reporting and investigating complaints, and outline disciplinary actions for perpetrators.
- Cultivating a Positive Workplace Culture: This involves promoting respect, empathy, and diversity, and rewarding positive interactions among employees. Leadership plays a critical role in setting the tone for acceptable behavior.
- Training and Education: Regular workshops or training sessions can help employees identify bullying, understand its impact, and learn how to respond effectively.
- Support Systems for Victims: Establishing support systems like counseling services, mediation, or conflict resolution strategies can help victims cope with the situation.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Regularly assess the effectiveness of anti-bullying measures and make necessary improvements based on feedback and observations.
Conclusion
Workplace bullying is a systemic issue that demands a systemic response. Addressing this silent epidemic requires continuous efforts from everyone within an organization, from top management to the newest recruit. By employees. Only by doing so can we hope to create a work environment that is safe, respectful, and conducive to growth and productivity for all.