Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a progressive lung disorder that affects millions of people worldwide, making it difficult for them to breathe. COPD is characterized by persistent respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation, which worsens over time. In this blog post, we’ll explore the various aspects of COPD, including its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options, as well as tips for living with this challenging condition.
Understanding COPD
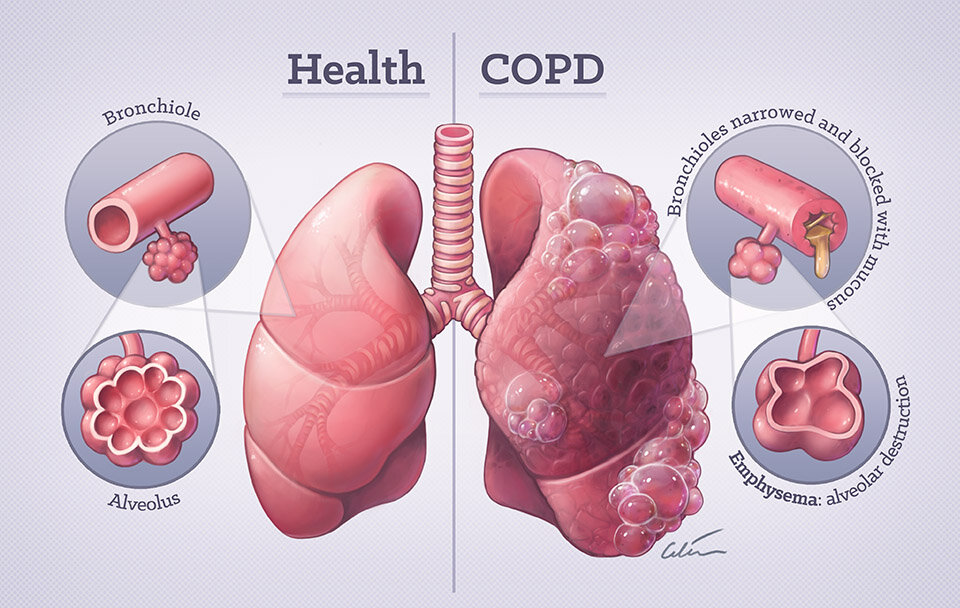
COPD is an umbrella term that includes two primary conditions: chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Chronic bronchitis involves long-term inflammation and thickening of the bronchial tubes, while emphysema damages the air sacs (alveoli) in the lungs. Both conditions lead to increased resistance in the airways, resulting in difficulty breathing and reduced lung function.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The most common symptoms of COPD include:
- Shortness of breath
- Chronic cough
- Wheezing
- Chest tightness
- Excess mucus production
- Fatigue
COPD is diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and lung function tests, such as spirometry, which measures the amount of air you can inhale and exhale. Imaging tests, like chest X-rays or CT scans, may also be used to assess the extent of lung damage.
Causes and Risk Factors
The primary cause of COPD is long-term exposure to lung irritants, such as:
- Tobacco smoke: Smoking is the most significant risk factor for COPD.
- Air pollution: Exposure to outdoor and indoor air pollution can contribute to COPD development.
- Occupational exposure: Workers in certain industries (e.g., mining, construction, and manufacturing) may be at higher risk due to exposure to dust, chemicals, and fumes.
- Genetics: A rare genetic disorder called alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency can increase the risk of developing COPD.
Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for COPD, the condition can be managed to slow its progression and alleviate symptoms. Treatment options include:
- Medications: Bronchodilators, inhaled corticosteroids, and combination inhalers can help open airways and reduce inflammation.
- Pulmonary rehabilitation: A structured program of exercise, education, and support to improve lung function and overall well-being.
- Oxygen therapy: Supplemental oxygen may be prescribed for those with severe COPD to maintain adequate blood oxygen levels.
- Vaccinations: Annual flu and pneumococcal vaccines can help prevent respiratory infections, which can worsen COPD symptoms.
Living with COPD
Managing COPD involves making lifestyle adjustments and adhering to your treatment plan. Here are some tips for living well with COPD:
- Quit smoking: Smoking cessation is the most important step to slow COPD progression and improve lung function.
- Stay active: Regular exercise can help maintain lung capacity and overall health.
- Avoid irritants: Minimize exposure to pollutants, chemicals, and allergens that can exacerbate COPD symptoms.
- Eat a healthy diet: A balanced diet can help support your immune system and maintain a healthy body weight.
- Stay connected: Join a support group or connect with others living with COPD to share experiences and tips for managing the condition.
COPD is a challenging and progressive lung disease that affects millions of people worldwide. However, by understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatments, and making lifestyle adjustments, you can effectively manage your condition and maintain a good quality of life. Be proactive about your health by adhering to your treatment plan, quitting smoking, and staying active. With the right knowledge and support, you can take control of your COPD and continue to live a fulfilling life.